|
Geothermal Heating & Cooling - General Info.
Who Can Use Geothermal?
How It Works
Types Of Systems
Application Examples
Benefits of Geothermal
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
How Does
It Work?
Two primary
components:
-
Water source heat pumps inside the building
-
Polyethylene pipe buried underground
outside the building or in a pond or lake. –An
environmentally-safe liquid circulates through the underground
pipe and acts as a heat exchanger. –In the winter, heat is
transferred from the ground to inside the building. –In the
summer, heat is extracted from the building and placed in the
ground
Types of
Geothermal Heating and Cooling Systems:
VERTICAL CLOSED LOOP

-
Most common configuration for commercial
buildings
-
Recommended where land area is limited
-
Pipes buried beneath a parking lot or lawn
area
-
150-220 feet of vertical drilling is needed
for each ton of heating and cooling capacity
HORIZONTAL
CLOSED LOOP

-
Recommended for smaller systems where there
is enough land to accommodate the pipes
-
Installed in trenches four to six feet deep
-
400-600 feet of pipe is required per ton of
heating and cooling capacity
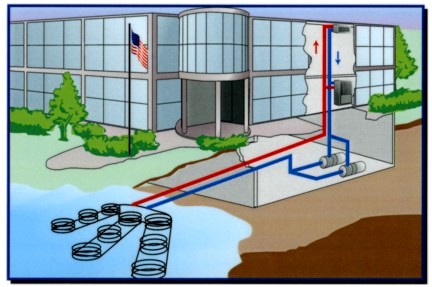
LAKE OR POND CLOSED LOOP
-
Recommended when a sufficient body of water
is nearby
-
Approximately 3,000 square feet of surface
area at a depth of 10 feet is required per ton of heating and
cooling capacity
LAKE OR POND SLIM JIM


|
|
Find out today what we can do
for you! |
 |
|
|
 |
International Ground Source
Heat Pump Association Member |
|
 |
Geothermal
Heat Pump Consortium Member |
|
|